What Is Epoxy Resin Made Of: Composition and Ingredients
Understanding Epoxy Resins
What Are Epoxy Resins?
Epoxy resins are a class of reactive prepolymers and polymers which contain epoxide groups. They are formed when you react epichlorohydrin (ECH) with bisphenol A, resulting in bisphenol A diglycidyl ether (Wikipedia). These resins can be cross-linked with various co-reactants such as polyfunctional amines, acids, phenols, alcohols, and thiols, creating thermosetting polymers known for their favorable mechanical properties, and high thermal and chemical resistance. Epoxy adhesives are integral in high-strength applications like the construction of aircraft, automobiles, and boats.
For an in-depth guide on how to use epoxy resin, check out our article on how to use epoxy resin.
Properties and Applications
Epoxy resins boast several properties that make them highly versatile:
- Mechanical Strength: Epoxy resins are known for their strong adhesive qualities, offering superior mechanical strength. They are often used in construction and manufacturing for applications that require durable bonding.
- Thermal Resistance: These resins can withstand high temperatures, making them suitable for environments where heat resistance is essential.
- Chemical Resistance: Epoxy resins are resistant to various chemicals, including acids and solvents. This makes them ideal for industrial applications where exposure to harsh substances is common.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Mechanical Strength | High strength bonds for robust applications |
| Thermal Resistance | Withstand high temperatures |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to acids, solvents, and other chemicals |
Epoxy resins find extensive use in various fields:
- Construction: Used for their bonding strength in applications such as flooring, countertops, and structural repairs.
- Automotive: Essential in car manufacturing for their superior adhesion and thermal resistance.
- Aerospace: Utilized in aircraft for their lightweight and strong bonding properties.
- Electronics: Widely applied in motors, generators, insulators, and printed circuit boards for their electrical insulation capabilities.
For home renovators interested in exploring more about epoxy resins, you may visit our articles on how to epoxy resin a table top and how to sand and polish epoxy resin.
By understanding what epoxy resins are and their remarkable properties, you can better appreciate their versatility and know-how to integrate them into your home renovation projects. For further reading on epoxy resin applications and benefits, see our guide on what is epoxy resin.
Composition of Epoxy Resins
To understand what epoxy resin is made of, it’s essential to delve into its composition. Epoxy resins are a type of adhesive with unique properties that make them incredibly versatile. Here’s what you need to know about the key components and types of epoxy resins.
Key Components
Epoxy resins consist of several key components that interact to form a durable and strong adhesive. Knowing these ingredients will help you better understand their applications.
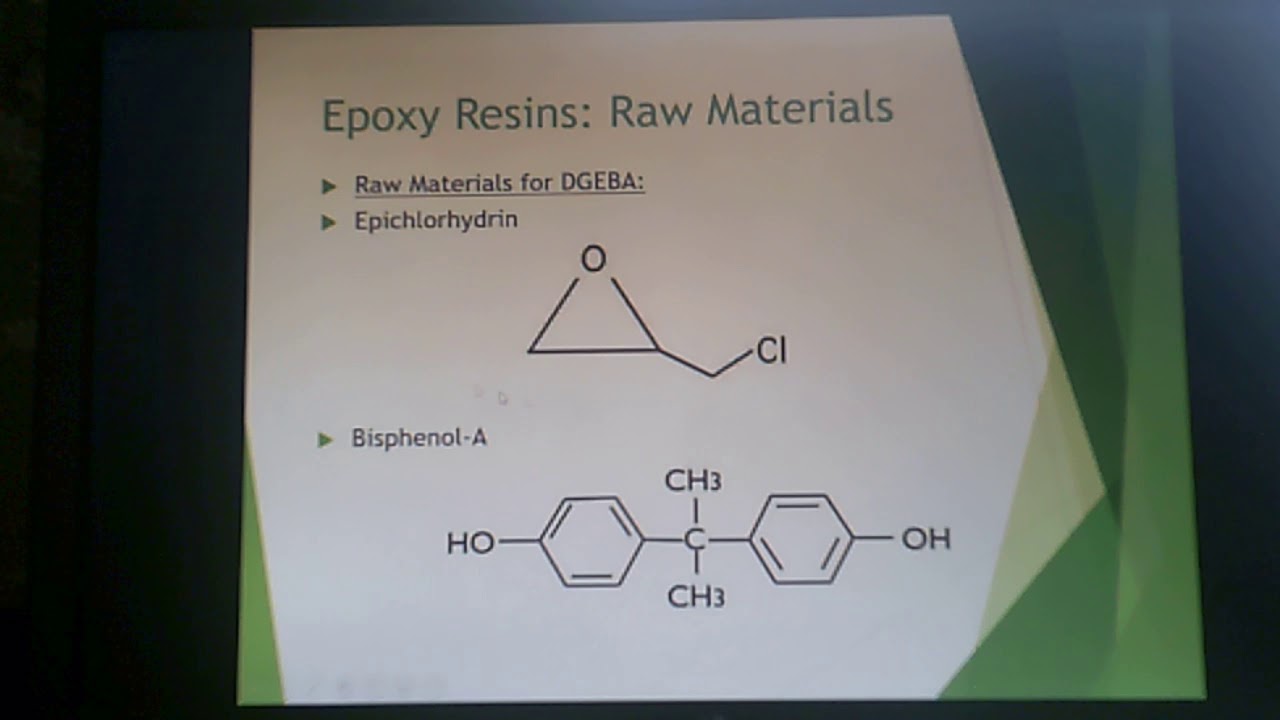
Epoxide Resin: The primary ingredient is the epoxide resin, also known as the epoxy prepolymer. This component contains epoxide groups, which are reactive molecules essential for the curing process. Glycidyl-based epoxy resins, like diglycidyl ether of bisphenol A (DGEBA), are widely used and produced through reactions involving epichlorohydrin and bisphenol A.
Hardeners (Curatives): Co-reactants, commonly called hardeners or curatives, are essential for turning the liquid resin into a solid. These include polyfunctional amines, acids, phenols, alcohols, and thiols. The reaction between the epoxy resin and the hardener results in a thermosetting polymer with favorable mechanical and thermal properties (Resin Library).
Fillers and Additives: Some epoxy resin products incorporate fillers such as quartz sand or other aggregates for added structural support. While most modern epoxy resins are solvent-free, additives can still be included for specific applications, like metal coatings (Wikipedia).
Table of Key Components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Epoxide Resin | Contains epoxide groups; base of the resin |
| Hardeners | Co-reactants like amines, acids that cross-link epoxy molecules |
| Fillers | Additional support, often used in construction environments |
| Additives | Specific function enhancements, such as solvents for metal coatings |
For more information on the curing process, see our section on how to cure epoxy resin.
Types of Epoxy Resins
Epoxy resins are categorized based on their chemical composition and intended applications. Here are the main types you might encounter:
Glycidyl Epoxy Resins: These are derived from the reaction of hydroxy groups with epichlorohydrin, resulting in glycidyl ethers (for alcohols/phenols) or glycidyl esters (for acids). Glycidyl ethers are the most common type and are exemplified by DGEBA, widely used in many applications.
Novolac Epoxy Resins: Produced from the reaction of phenol-formaldehyde novolac with epichlorohydrin. These resins exhibit higher cross-linking density, providing higher thermal and chemical resistance.
Aliphatic Epoxy Resins: These resins feature aliphatic groups, which entails that the structural backbone does not have aromatic rings. They are used for applications requiring flexibility and durability.
Cyloaliphatic Epoxy Resins: Similar to aliphatic epoxy resins but including cycloaliphatic compounds. They are known for their high strength and electrical insulating properties.
| Type | Key Characteristics | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Glycidyl Epoxy Resins | Good for general use, versatile | Adhesives, coatings, composites |
| Novolac Epoxy Resins | High thermal and chemical resistance | Electrical parts, high-temp adhesives |
| Aliphatic Epoxy Resins | Flexibility, durability | Protective coatings, sealants |
| Cycloaliphatic Epoxy Resins | High strength, excellent electrical insulating properties | Electronics, electrical encapsulations |
Understanding the different types of epoxy resins will enable you to choose the best one for your home renovation projects. For tips on how to use these versatile adhesives, you can visit our guide on how to use epoxy resin.
By grasping the composition and variations of epoxy resins, you can make informed choices for your DIY tasks or professional projects. Whether you’re sealing sand in epoxy resin or exploring its curing process, your knowledge of these essential components and types will serve you well.
Production and Manufacturing
Understanding how epoxy resin is made involves diving into both the synthesis process and the raw materials used in its production. Let’s break down these elements to give you a clearer picture.
Synthesis Process
The synthesis of epoxy resin is a detailed procedure that typically begins with the creation of Bisphenol-A diglycidyl ether (DGEBA), the most commonly used epoxy in various industries. This is created through a chemical reaction between bisphenol-A and epichlorohydrin (Sakshi Chem Sciences). The following key steps encapsulate the process:
- Reaction Initiation: Bisphenol-A and epichlorohydrin are introduced into a reactor. The mixture is heated and stirred to start the chemical reaction.
- Formation of Epoxide Groups: The reaction produces epoxide groups, which are responsible for the adhesive and mechanical properties of the resin.
- Purification: The resulting mixture is purified to remove any unreacted materials and by-products.
- Curing: The final step involves adding a curing agent or hardener, which initiates the solidification process when the resin is applied to a surface. The mixture ratios for epoxy resins are usually 2:1 or 4:1, depending on the intended application (Bisley Company).
Raw Materials
The base of epoxy resins primarily includes raw materials sourced from petroleum, although plant-derived materials are being increasingly utilized. Key raw materials needed for epoxy resin production are:
- Epoxy Resin: Made up of a blend of epoxide groups and other molecules.
- Curing Agents: These are essential for initiating the curing process and typically added in small amounts (2-5% of the total epoxy resin weight).
- Fillers and Additives: Added to improve specific properties like viscosity, adhesion, and durability.
| Raw Material | Source | Percentage in Mixture |
|---|---|---|
| Epoxy Resin | Petroleum/Plant-Derived | 95-98% |
| Curing Agents | Synthetic Compounds | 2-5% |
| Fillers/Additives | Various Sources | 0-3% |
Types of Epoxy Resins
There are three major types of epoxy resins:
- Phenolic Glycidyl Ethers: Known for high mechanical strength and excellent adhesion.
- Aromatic Glycidyl Amines: Renowned for their superior heat resistance and chemical stability.
- Cycloaliphatics: Preferred for their low viscosity and better UV resistance (Omnexus).
Each type of epoxy resin has distinct properties and applications, making it vital to choose the right type depending on your specific needs.
Explore more about different types of epoxy resins and their applications in our article on what is epoxy resin.
For further details on safely using and handling epoxy resin, check out our guides on how to use epoxy resin and how long does it take for epoxy resin to dry.
Curing Process of Epoxy Resins
Once you understand what epoxy resin is made of, it’s essential to know how it cures. The curing process transforms the liquid resin into a solid, durable material. Let’s explore the chemical reaction and the essential curing agents and additives.
Chemical Reaction
The curing of epoxy resin involves a fascinating chemical reaction. When the epoxy resin and a hardener are mixed, they undergo a transformation from liquid to solid. This process, called polymerization, converts the individual molecules into a three-dimensional network, giving the cured epoxy its strength and durability. The chemical reaction includes several stages:
-
Liquid State: Initially, the resin and hardener mixture remains in a liquid, workable state known as the open time. During this period, you can pour, shape, and clamp the epoxy to ensure a reliable bond. Proper preparation and sanding are necessary before recoating once the epoxy begins to harden (WEST SYSTEM).
-
Gel State: As the reaction progresses, the mixture thickens and reaches a gel consistency. At this point, the epoxy is partially cured but still flexible.
-
Solid State: Eventually, the epoxy hardens completely, achieving about 90% of its final strength. The curing process can continue at room temperature for several days until it is fully cured (WEST SYSTEM).
Cure Stage State Workability Liquid Workable Can be poured, shaped, and clamped Gel Partially Cured Flexible but thick Solid Fully Cured Final strength achieved
Curing Agents and Additives
The curing process relies on specific agents and additives that enhance the performance and properties of the epoxy resin.
-
Curing Agents: These are chemicals known as hardeners that initiate the curing reaction when mixed with the epoxy resin. The speed of curing can vary based on the type of hardener used:
- Slow Curing Agents: Ideal for large projects requiring extended working time.
- Fast Curing Agents: Best for smaller projects or lower temperatures where a quicker cure is desired.
-
Additives: Various additives can be mixed into the epoxy to tailor its properties for specific applications:
- Fillers: Used to thicken the resin, making it suitable for gap filling and bonding.
- Pigments: Added to color the epoxy for aesthetic or identification purposes. Read more about how to add color pigment to epoxy resin.
- Accelerators: Chemicals that decrease the cure time by speeding up the reaction.
To better manage your epoxy projects, it’s important to be aware of the factors affecting cure time, such as temperature and hardener selection. For example, warm temperatures can accelerate curing, while cooler conditions might require a faster hardener or additional heat (WEST SYSTEM).
Always take precautions during the curing process, such as avoiding pouring epoxy thicker than ½” to prevent excessive heat generation that could damage your project or melt containers.
By understanding the curing process of epoxy resins, you can achieve exceptional results for your home renovation projects. For more insights, visit our article on how to cure epoxy resin and discover valuable tips for safe and effective epoxy use.
Advantages and Versatility
Epoxy resins offer numerous benefits that make them a popular choice for various applications, from home renovations to industrial use. Understanding these advantages can help you make the most out of this versatile material.
Benefits of Epoxy Resins
Epoxy resins bring several advantages to the table due to their unique properties and composition. Here’s a detailed look at what makes them so beneficial:
-
Strong Adhesion: Epoxy resins exhibit exceptional bonding capabilities, enabling them to adhere well to a variety of substrates including concrete, wood, and metals. This makes them ideal for diverse applications such as epoxy resin table tops and repair work.
-
Durability: Known for their high toughness and resistance to wear and tear, epoxy resins are perfect for applications requiring long-lasting performance. They are highly resistant to impact, making them suitable for both indoor and outdoor use.
-
Chemical Resistance: Epoxy resins offer excellent resistance to a wide range of chemicals, including acids, bases, and solvents (Bisley Company). This property is particularly useful in industrial settings where exposure to harsh chemicals is common.
-
Low Shrinkage: When cured, epoxy resins exhibit minimal shrinkage, which helps maintain the integrity of the bond and ensures a smooth, even finish (Science Direct).
-
Favorable Viscosity: The viscosity of epoxy resins makes them easy to apply over different surfaces. This characteristic is crucial for applications requiring a smooth and even coating.
-
Environmental Resistance: Epoxy resins are highly resistant to environmental factors such as moisture, heat, and UV light, which makes them suitable for outdoor projects.
Versatile Applications
Due to their advantageous properties, epoxy resins find extensive use in a multitude of applications. Here are some of the most common ways you can use epoxy resins:
-
Adhesives: Given their strong bonding capabilities, epoxy resins are widely used as adhesives in various sectors, from home repairs to aerospace industries. They can adhere to substrates like wood, metal, and concrete, offering robust and reliable bonds.
-
Electronics: Epoxy resins are a crucial component in electronic manufacturing due to their excellent electrical resistivity and ability to protect components from environmental and chemical damage. They are commonly used in encapsulating electronic circuits and components.
-
Aerospace: In the aerospace industry, epoxy resins serve as matrices for composites used in the manufacturing of aircraft parts. Their high strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to environmental factors make them ideal for this demanding applications.
-
Flooring: Epoxy resin flooring is popular in both commercial and residential settings due to its durability, ease of cleaning, and aesthetically pleasing finish. It’s also resistant to chemicals and stains, making it a practical choice for spaces like garages and basements.
-
Art and Crafts: Epoxy resins provide a clear, glossy finish, making them a favorite among artists and DIY enthusiasts for creating jewelry, tabletops, and other decorative items. For tips on adding color pigments to your epoxy resin projects, see how to add color pigment to epoxy resin.
-
Sealant: Epoxy resins make effective sealants due to their strong adhesion and chemical resistance. They are commonly used for sealing cracks and leaks in materials such as concrete and metals. For guidance on sealing sand, see can you seal sand in epoxy resin.
Epoxy resins can cater to a wide array of needs, offering both functional and aesthetic benefits. Whether you’re looking for strong adhesives or a durable finish, understanding the advantages and versatile applications of epoxy resins can help you make the most of this material in your projects.
Industry Insights
Global Market Overview
The global epoxy resin market has seen significant growth and is expected to continue expanding. The market size is projected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 6.3% from 2020 to 2025 (NIIR). In 2016, the global epoxy resin market was valued at approximately $8 billion. Notably, the Asia-Pacific region dominates the market, contributing 55.2% of the total market share with China as the major producer and consumer, accounting for almost 35% of the global production.
| Year | Market Value (Billion USD) | Projected CAGR (2020-2025) |
|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 8.0 | 6.3% |
Epoxy resins play a crucial role across various industries, including construction, automotive, wind energy, and electronics. These industries drive the demand for epoxy resins, significantly contributing to the global market growth. For more detailed information on epoxy resins and their applications, check out our guide on what is epoxy resin.
Industry Applications and Trends
Epoxy resins are known for their versatility and are extensively used in multiple sectors for various applications. Here are some primary industry applications:
- Construction: The construction industry is a major consumer of epoxy resins. They are used in flooring, coatings, and adhesives due to their strong bonding and durable properties (NIIR).
- Automotive: Epoxy resins are utilized in the automotive industry for paint, composites, and adhesives. Their robust bonding feature is crucial in vehicle assembly, ensuring durable and strong joints.
- Wind Energy: In the wind energy sector, epoxy resins are essential for blade coating and repair, contributing to the longevity and efficiency of wind turbine blades (NIIR).
- Electronics: Epoxy resins serve as encapsulation materials for electronic devices, providing excellent electrical insulation and protecting components from dust, moisture, and short circuiting. Explore more about the applications of epoxy resins in electronics here.
| Industry | Primary Applications |
|---|---|
| Construction | Flooring, coatings, adhesives |
| Automotive | Paint, composites, adhesives |
| Wind Energy | Blade coating, repair |
| Electronics | Encapsulation, insulation, PCB coating |
Epoxy systems are also significant in aerospace applications, where they act as bonding matrix materials reinforced by fibers like glass, carbon, Kevlar, and boron (Wikipedia). They provide strong bonds necessary for aircraft construction and other high-strength adhesive applications.
For more insightful articles on epoxy resin, such as how to add color pigment to epoxy resin or how to polish epoxy resin, click on the provided internal links.