Types of PVC Glue: A Comprehensive Guide for All Projects
When working on PVC projects, choosing the right glue can make all the difference. With various types of PVC glue available, each designed for specific applications, it’s crucial to know which one suits your needs. Whether you’re tackling a plumbing repair or crafting a DIY project, understanding these adhesives will ensure a strong, lasting bond.
You’ll encounter solvent cements, transition cements, and specialty adhesives in your search. Each type has unique properties and uses, making it essential to match the glue to your project’s requirements. Let’s jump into the different types of PVC glue and discover which one is perfect for you.
Key Takeaways
- Understand Different PVC Glues: Knowing the types of PVC glues, such as solvent cements, transition cements, and specialty adhesives, is essential for choosing the right one for your project.
- Color-Coded Cements: Different colors like Blue, Aqua Blue, Orange, and Yellow indicate specific application areas and features. For instance, Blue is fast-setting while Orange is used for cold weather applications.
- Applications and Properties: Each type of PVC glue is designed for unique applications, from residential plumbing and potable water systems to high-pressure industrial uses.
- Factors to Consider: When selecting PVC glue, consider pipe material, size, environmental conditions, and local building codes to ensure a strong and compliant bond.
- Proper Usage Techniques: Ensuring a strong bond involves cleaning the pipes, applying glue evenly, joining the pieces quickly, and allowing sufficient drying time.
- Alternatives to PVC Glue: CPVC glue and PVC primer offer alternatives for specific applications requiring higher temperature resistance or stronger adhesion.
What is PVC Glue?
PVC glue, more accurately known as PVC solvent cement, is a chemical solvent designed to bond PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) pipes and fittings. It plays a crucial role in plumbing and various DIY projects, offering a seamless and permanent connection between PVC components. Let’s investigate deeper into its function and different types.

Function and Mechanism
PVC solvent cement works through a chemical reaction. It effectively melts the surface of the PVC pipe and fitting, creating a fusion that results in a strong and permanent bond. This process is often termed “cold welding” as it achieves the connection without the need for heat.
Types of PVC Solvent Cement
PVC glue comes in several types, each formulated for specific conditions and applications. The following sections detail the primary variants you might encounter:
Color-Coded Cements
Different colors indicate the specific type of PVC solvent cement and its respective application areas:
- Blue: Fast-setting cement, suitable for general purposes and damp conditions. Ideal for quick projects requiring rapid curing.
- Aqua Blue: Specifically designed for use in water or damp environments, providing a reliable bond even when moisture is present.
- Orange: Formulated for cold weather applications, this type is also used for CPVC (Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride) pipes which require a higher strength bond.
- Yellow: A one-step cement used for CPVC that, in some jurisdictions, doesn’t require a primer, simplifying the bonding process.
Table of PVC Solvent Cement Types
| Color | Application Area | Special Features |
|---|---|---|
| Blue | General, Damp Conditions | Fast-setting, Rapid Curing |
| Aqua Blue | Water, Moist Environments | Moisture-resistant, Reliable in Wet Conditions |
| Orange | Cold Weather, CPVC Pipes | Cold Weather Use, High Strength for CPVC |
| Yellow | CPVC Pipes | Primer Not Required in Some Jurisdictions |
Summary
Understanding the various types of PVC solvent cement ensures that you select the right glue for your specific project needs. Proper selection leads to a strong and durable bond, critical for the longevity and reliability of your PVC installations. Always match the cement type to the environmental conditions and material specifications to achieve the best results.
Types of PVC Glue
Choosing the right PVC glue ensures a robust and lasting bond for your projects. We’ll investigate into the key types, emphasizing their specific applications.
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) Cement
PVC cement, or solvent cement, bonds PVC pipes and fittings by chemically softening the PVC surface.
Applications:
- Residential and commercial plumbing
- Potable water systems
- Pressure pipes
- Drainage, waste, and vent (DWV) applications
Types of PVC Cement:
- Blue PVC Cement: Fast-setting, good for quick applications.
- Clear PVC Cement: Fast-drying, used for potable water, pressure pipes, and DWV.
- Gray PVC Cement: Best for larger diameter pipes and high-pressure industrial uses.
CPVC (Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride) Cement
CPVC cement is designed for CPVC pipes, enduring higher temperatures and pressure than regular PVC.
Applications:
- Hot and cold water distribution
- Industrial liquid handling
Types of CPVC Cement:
- Orange CPVC Cement: Suitable for both residential and industrial hot water systems.
- Yellow or One-Step CPVC Cement: Doesn’t require a primer in some jurisdictions.
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) Cement
ABS cement bonds ABS pipes and fittings, known for high impact strength and good temperature performance.
Applications:
- Drainage systems
- Waste and vent systems
Types of ABS Cement:
- Black ABS Cement: Standard for most ABS piping applications.
- Transition ABS Cement: Used for specific pipe transitions involving different materials.
Transition Cement
Transition cement is crucial when joining different types of plastic pipes, such as PVC to ABS.
Applications:
- Mixed-material plumbing
- Repairs involving multiple plastic pipe types
- Best for multi-material pipe systems
- Common in repair scenarios
Understanding the distinct uses and benefits of each type can help you choose the optimal glue for your needs. For reliable results, align the glue type with your specific application.
Factors to Consider When Choosing PVC Glue
Selecting the right PVC glue depends on several factors to ensure a strong, lasting bond. Not all PVC glues are the same; each type matches specific conditions and materials.
Pipe Material
Your choice should align with the pipe material for effective bonding.
- PVC Pipes: Use PVC cement for polyvinyl chloride pipes. It’s designed to work exclusively with PVC material.
- CPVC Pipes: CPVC cement is necessary for chlorinated polyvinyl chloride pipes, which withstand higher temperatures.
- ABS Pipes: ABS cement suits acrylonitrile butadiene styrene pipes, common in drainage systems.
Each adhesive type chemically reacts with its target material, hence matching them correctly ensures durability.
Pipe Size and Diameter
The size and diameter of pipes influence the type of glue and its application method. Larger pipes usually demand a thicker layer of adhesive and sometimes a different type altogether.
- Small Diameter Pipes: Easier to bond, quick-setting glues like blue PVC cement are suitable.
- Large Diameter Pipes: Require more glue and often need a slower-setting type to ensure complete coverage and bonding.
Application Conditions
Consider the environmental conditions where the glue will be applied and the pipe system will operate.
- Temperature: Use orange CPVC cement for cold weather to ensure proper bonding in low temperatures.
- Moisture: Aqua blue PVC cement performs well in wet conditions.
- Time-sensitive Repairs: Opt for fast-setting cements like the blue PVC variant for quick fixes.
Local Codes and Standards
Compliance with local plumbing codes and standards is crucial. Different jurisdictions may have specific regulations about the types of adhesives suitable for various applications.
- Building Codes: Check local building codes to know the appropriate type of cement.
- Regulations: Some areas may require primers while others accept one-step glues like yellow CPVC cement.
- Inspections: Ensure your glue choice meets inspection standards to avoid project delays or rework.
By considering these factors—material type, pipe size, application conditions, and local regulations—you can select the right PVC glue, ensuring robust, compliant, and enduring joint connections.
How to Use PVC Glue
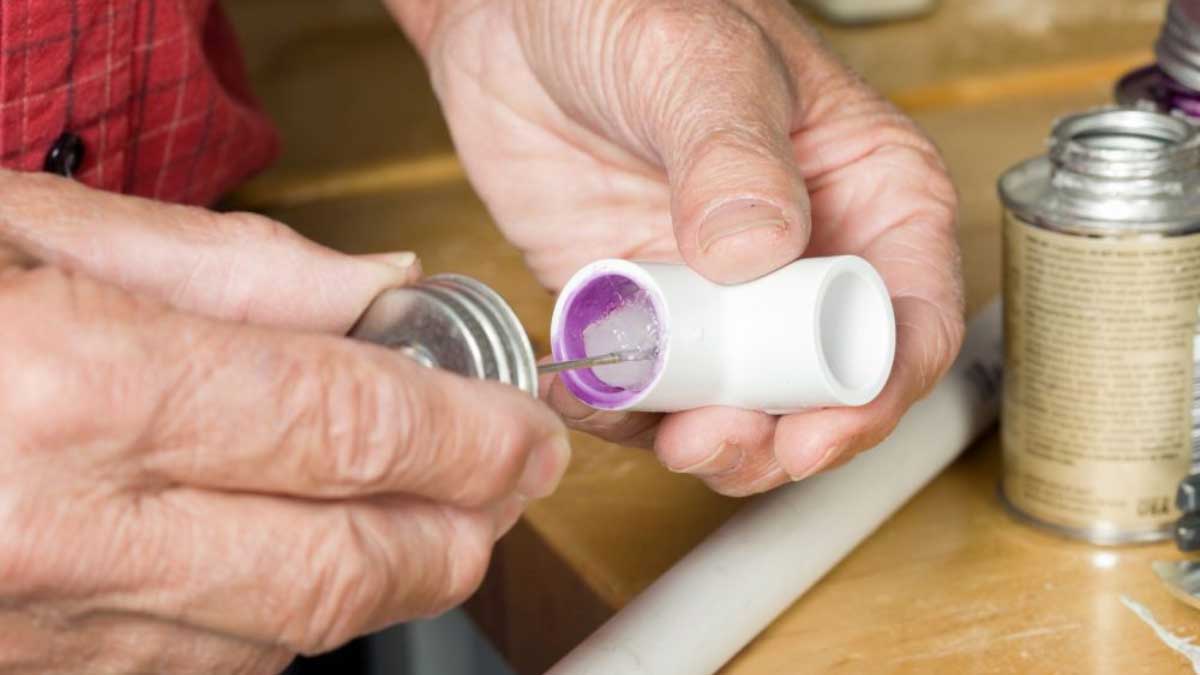
PVC glue, known as solvent cement, bonds PVC pipes and fittings securely. Here’s a step-by-step guide to ensure a strong and lasting connection.
Step 1: Clean the Pipes
Dirt, grease, and moisture compromise the bond strength. Use a clean, dry cloth to wipe the ends of the pipes and fittings. For stubborn dirt or oil, use a PVC cleaner or primer.
Step 2: Apply the Glue
Brush the PVC glue evenly onto both pipe ends. Ensure a thorough yet even coat to cover the entire surface. Use the recommended brush size for your pipe diameter.
Step 3: Join the Pieces
Once the glue is applied, quickly insert the pipe into the fitting. Push the pipe all the way in and give it a quarter-turn to evenly distribute the glue. Hold in place for 30 seconds.
Step 4: Let the Joint Dry
Allow the joint to dry completely before pressurizing or using the system. Generally, wait 15 minutes for fast-drying glue and 24 hours for full strength.
Summary
By cleaning the pipes, applying the glue evenly, joining the pieces promptly, and allowing the joint to dry, you’ll achieve a robust and durable bond.
Alternatives to PVC Glue
When you’re working with PVC materials, you might need alternatives to traditional PVC glue for specific reasons. Here, we’ll explore some viable options.
CPVC Glue for PVC Pipes
CPVC Glue:
- Definition: A chemical solvent specifically formulated to bond CPVC (Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride) pipes and fittings.
- Properties: Resilient to higher temperatures and pressures compared to regular PVC glue.
- Usage: Often used in hot and cold water systems, industrial applications, and when chemical resistance is required.
Advantages:
- Higher Temperature Resistance: Handles temperatures up to 200°F, making it suitable for hot water systems.
- Versatile: Works well with both CPVC and PVC materials.
- Durable: Creates a strong, long-lasting bond.
Examples:
- Orange CPVC Cement: Requires primer unless local codes allow a one-step process. Suitable for both cold and hot water systems.
- Yellow CPVC Cement: One-step cement that doesn’t need primer if local regulations permit, ideal for cold and hot potable water pipes.
Step-by-Step Usage:
- Clean the Pipes: Remove any dirt, grease, and moisture from the pipe surfaces.
- Apply Primer: If required, apply to both the pipe and fittings.
- Apply CPVC Glue: Spread it evenly around the pipe and fitting surfaces.
- Join Pipes: Push them together and hold for a few seconds.
- Allow to Dry: Follow manufacturer’s recommendations for drying times.
PVC Primer As a Substitute
PVC Primer:
- Definition: A chemical cleaner that softens and prepares PVC surfaces for gluing.
- Properties: Ensures a stronger bond by pre-softening the material, allowing the solvent cement to penetrate more effectively.
- Usage: Essential for projects where a strong, reliable bond is crucial, such as in plumbing systems.
Advantages:
- Increases Adhesion: Creates a better surface for the cement to adhere to.
- Ensures Clean Bonding Surface: Removes contaminants that could weaken the bond.
- Versatile: Compatible with various types of PVC cements.
Examples:
- Purple Primer: Visibly shows where it’s applied. Often required by building codes.
- Clear Primer: Less visible but equally effective.
Step-by-Step Usage:
- Clean Surfaces: Clear any debris or moisture from the pipe surfaces.
- Apply Primer: Spread it on both the pipe and the fitting surfaces.
- Inspect: Ensure the primer has created a uniform, soft surface.
- Apply Glue: Follow up with the appropriate PVC glue type.
- Join Pipes: Press the pipes together quickly after applying the glue.
- Drying Time: Let the joint cure as per the glue manufacturer’s instructions.
Data-Rich Table:
| Material Type | Temperature Resistance | Application Areas | Required Primer Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Orange CPVC | Up to 200°F | Hot & cold water systems, industrial applications | Yes, unless local codes allow none |
| Yellow CPVC | Up to 200°F | Cold & hot potable water pipes | No, if local codes permit |
| Purple Primer | Not applicable | Any project requiring visible verification of primer | Yes, often required by codes |
| Clear Primer | Not applicable | Projects where appearance is a factor | Yes |
By considering CPVC glue and PVC primer, you can find suitable alternatives for PVC glue in various applications. Adjust your choice based on the specific requirements and local regulations of your project.
Conclusion
Choosing the right PVC glue is essential for the success of your PVC projects. By understanding the different types of PVC adhesives and their specific applications, you can ensure a strong and lasting bond. Matching the glue to your project needs, considering factors like material type, pipe size, and application conditions, will help you achieve the best results.
Always comply with local plumbing codes and standards to ensure safety and durability. Proper application techniques, including cleaning and priming, are crucial for a robust connection. Whether you’re using traditional PVC solvent cement, CPVC glue, or PVC primer, selecting the appropriate adhesive will lead to a successful and enduring project.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is PVC glue used for?
PVC glue, or PVC solvent cement, is used to bond PVC pipes and fittings. It creates a strong, permanent connection by melting the surfaces together, a process known as “cold welding.”
How do I choose the right PVC glue?
To choose the right PVC glue, consider the pipe material (PVC, CPVC, or ABS), pipe size, application conditions such as temperature and moisture, and local plumbing codes.
What are the different types of PVC glue?
There are several types of PVC glues including PVC cement, CPVC cement, ABS cement, and transition cement. Each type is designed for specific materials and applications.
Why is PVC glue color-coded?
PVC glues are color-coded for specific applications: blue for general use, aqua blue for moist environments, orange for cold weather and CPVC pipes, and yellow for CPVC pipes that might not require a primer.
Can I use PVC glue in cold weather?
Yes, there are specific PVC glues formulated for cold weather, such as orange CPVC cement designed for applications in lower temperatures.
What is the difference between PVC and CPVC glue?
PVC glue is used for general PVC piping systems, while CPVC glue is formulated for higher temperature and pressure applications, such as hot water systems.
Do I need to use a primer with PVC glue?
Using a primer is highly recommended as it softens the material, ensuring a stronger bond. Some PVC cements are designed to work without a primer, but always check local codes and manufacturer recommendations.
How do I apply PVC glue?
Start by cleaning the pipes, then apply the glue evenly on both surfaces to be joined. Quickly join the pieces and hold them together until the bond sets. Allow the joint to dry adequately before use.
What are alternatives to PVC glue?
Alternatives to PVC glue include CPVC glue for higher temperature applications and PVC primer that prepares surfaces for gluing by increasing adhesion.
Is PVC glue safe for potable water?
Yes, certain PVC glues are formulated to meet safety standards for potable (drinking) water. Always check the product specifications to ensure it is safe for your intended use.