Shoe Goo vs Rubber Cement: Best Adhesive for Shoe Repair?
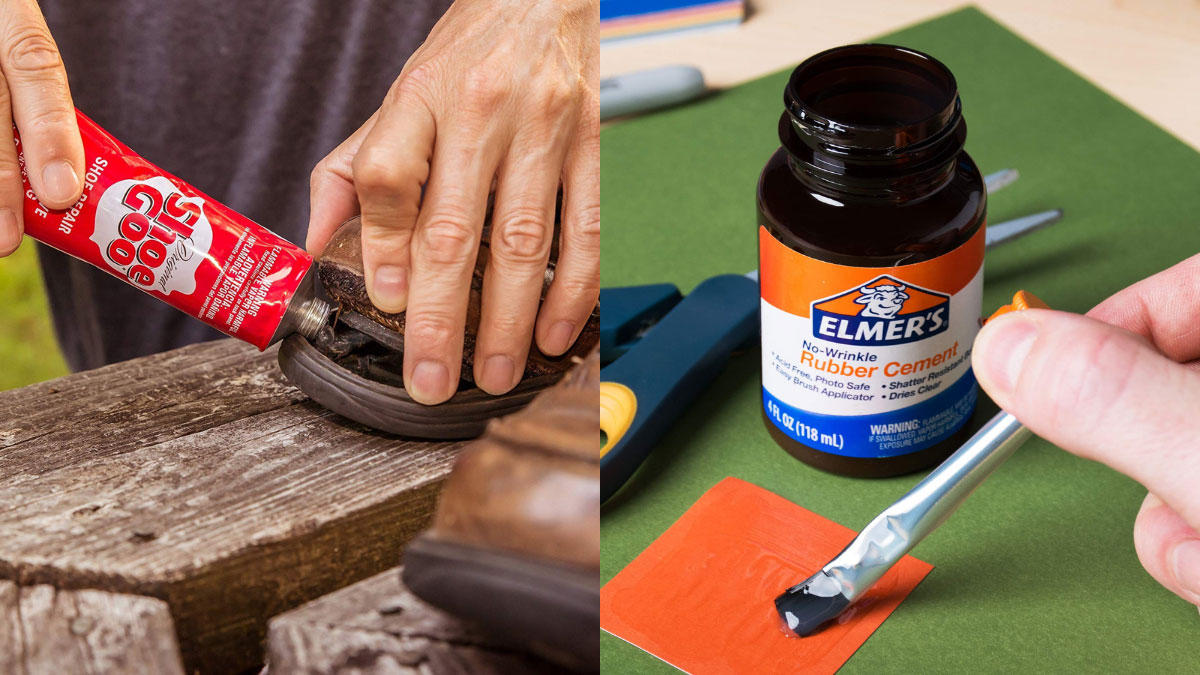
When your favorite pair of shoes starts to fall apart, you might wonder whether to reach for Shoe Goo or rubber cement. Both products promise to extend the life of your footwear, but which one truly delivers? Understanding the differences between these two adhesives can help you make the best choice for your shoe repair needs.
Shoe Goo and rubber cement both have their strengths and weaknesses. Shoe Goo is known for its durability and flexibility, making it ideal for high-wear areas. On the other hand, rubber cement offers a quick fix that’s easy to apply but may not hold up as well over time. By comparing their features, you’ll be better equipped to decide which product suits your specific situation.
Key Takeaways
- Durability and Flexibility: Shoe Goo offers superior durability and flexibility, making it ideal for high-wear areas such as shoe soles and edges, whereas rubber cement is better suited for temporary and low-stress fixes.
- Material Versatility: Shoe Goo is highly versatile and effective on various materials including rubber, leather, and synthetic fabrics, while rubber cement works best on lightweight, flexible materials like paper and foam.
- Bond Strength: Shoe Goo provides a stronger, more permanent bond, but rubber cement is easier to remove and reposition, making it better for projects where flexibility and temporary fixes are needed.
- Application and Drying Time: Shoe Goo requires thorough surface preparation and takes 24-72 hours to cure fully, whereas rubber cement allows for quick and easy application with a faster drying time within minutes.
- User Experience: Customer reviews highlight Shoe Goo’s effectiveness for long-term repairs and versatility, despite its strong odor, while rubber cement is praised for quick fixes but criticized for its weaker bond strength and limited durability.
Key Features
Understanding the key features of Shoe Goo and rubber cement can help you make an well-informed choice for your shoe repair needs. Each product has distinct characteristics that make it suitable for specific applications.
Shoe Goo
Purpose:
- Primarily used for repairing footwear, particularly for bonding and sealing shoe components.
Durability:
- Known for its abrasion resistance and flexibility. Shoe Goo holds up well in high-wear areas.
Versatility:
- Can be used on various materials, such as rubber, wood, glass, concrete, and metal.

Rubber Cement
Purpose:
- Commonly used for quick fixes on shoes, providing an easy and temporary solution for small repairs.
Durability:
- Less durable than Shoe Goo. It may not hold up as well in high-stress areas but is effective for low-impact repairs.
Versatility:
- Generally suitable for flexible materials like paper and rubber but less effective on dense or hard materials.
Composition
Shoe Goo
Synthetic Rubber:
- Contains styrene-butadiene, providing good abrasion resistance.
Solvents:
- Includes toluene or tetrachloroethylene and solvent naphtha, which act as cleaning and degreasing agents.
Rubber Cement
Natural Rubber Latex:
- Composed of natural rubber latex, offering flexibility and ease of application.
Solvent Base:
- Utilizes a solvent such as heptane or hexane to keep the adhesive in a liquid state until applied.
Application Methods
Shoe Goo
- Preparation: Clean and degrease the surfaces to be bonded. Ensure they are dry before application.
- Application: Apply a thin layer to the surfaces. Allow it to dry until tacky before pressing the surfaces together.
- Preparation: Clean the surfaces to ensure they are free from dust and debris.
- Application: Apply a thin layer of rubber cement to both surfaces. Allow it to dry slightly before pressing the surfaces together.
Understanding these features and application methods will guide you in choosing the right adhesive for your shoe repair projects.
Performance Comparison
When considering shoe repair adhesives, understanding the performance differences between Shoe Goo and rubber cement is crucial.
Bond Strength
- Shoe Goo: Known for its robust and adaptable bonding properties, Shoe Goo excels in shoe repairs. It forms a durable bond, withstanding various conditions like water and temperature changes. Suitable for materials like leather, rubber, and other flexible components, it cures in about 24 hours, reaching maximum strength within 48 to 72 hours.
- Rubber Cement: In contrast, rubber cement offers a weaker bond. It’s designed for easy removal without damaging items, making it less ideal for long-term shoe repairs. This adhesive doesn’t provide the permanent bond needed for critical repairs.
Flexibility and Durability
- Shoe Goo: Shoe Goo’s flexibility and durability stand out, making it perfect for repairs that require significant movement and resilience. It maintains integrity under stress, essential for high-wear areas like shoe soles and edges.
- Rubber Cement: Although rubber cement is flexible, it falls short in durability. It serves well for temporary fixes but doesn’t offer the long-lasting performance needed for worn-out shoes. Its composition, suited for minor and quick repairs, doesn’t support the same level of wear and tear as Shoe Goo.
| Feature | Shoe Goo | Rubber Cement |
|---|---|---|
| Bond Strength | Strong and Durable | Weaker, Temporary |
| Cure Time | 24-72 hours | Immediate to few minutes |
| Material Suitability | Leather, Rubber, Flexible Components | Flexible Materials |
| Durability | High | Low |
| Flexibility | High | Moderate |
Understanding these distinctions ensures you choose the right adhesive for your shoe repair needs, considering the specific requirements of the repair job.
Use Cases And Suitability
In choosing between Shoe Goo and rubber cement, understanding their specific use cases and suitability is crucial. Both adhesives serve distinct purposes, each with unique benefits and limitations.
Best Uses For Shoe Goo
- Flexibility and Abrasion Resistance: Shoe Goo excels in its flexibility and resistance to wear and tear. Comprising an abrasion-resistant synthetic rubber and a cleaning/degreasing solvent, it’s perfect for repairs needing flexibility and durability.
- Example: Repairing the soles of athletic shoes where high flexibility is needed.
- Shoe Sole Repairs: This adhesive works wonders for repairing separated components of shoes, filling worn shoe soles, and sealing waterproof fabrics and footwear. It bonds well with rubber, leather, and synthetic fabrics.
- Example: Attaching a loose sole to a leather hiking boot.
- Multi-Purpose Applications: Beyond shoes, Shoe Goo is versatile. Skateboarders use it to protect skate shoes, cyclists mend punctured inner tubes, and hobbyists repair various models. It’s also effective for waterproofing and protecting cricket bat toes.
- Example: Sealing a tear in a waterproof jacket.
Best Uses For Rubber Cement
- Quick and Temporary Fixes: Rubber cement offers a fast, easy solution for temporary repairs. Composed of natural rubber latex and a solvent base, it’s ideal for non-permanent fixes.
- Example: Quickly reattaching a paper label.
- Flexible Material Bonding: It’s adept at bonding lightweight, flexible materials without requiring a permanent fix.
- Example: Binding flexible foam sheets in arts and crafts.
- Non-Damaging Applications: The low bond strength makes rubber cement ideal when you need the option to remove or reposition bonded items without causing damage.
- Example: Mounting photos in a scrapbook.
| Feature | Shoe Goo | Rubber Cement |
|---|---|---|
| Key Component | Abrasion-Resistant Synthetic Rubber | Natural Rubber Latex |
| Typical Use | Permanent Repairs, Sole Reattachment | Temporary Fixes, Scrapbooking |
| Drying Time | 24 Hours for Initial Cure | Minutes |
| Bond Strength | High | Moderate |
| Flexibility | High | Low |
| Best Used on | Rubber, Leather, Synthetic Fabrics | Paper, Light Fabrics, Foam |
| Additional Characteristics | Waterproofing, Multipurpose | Easy Repositioning, Non-Damaging |
Understanding these distinctions helps you choose the right adhesive for your needs.
Pros And Cons
When deciding between Shoe Goo and rubber cement for your shoe repair needs, it’s important to understand the specific advantages and disadvantages of each product. Knowing these can help you make a more well-informed choice based on your specific requirements.
Advantages Of Shoe Goo
Shoe Goo offers several notable benefits:
- Versatile Use: Effective for various materials, including rubber, wood, glass, concrete, and metal. Ideal for repairing separated shoe components, filling worn soles, and sealing waterproof fabrics.
- Abrasion Resistance: Contains styrene-butadiene, a synthetic rubber known for its durability and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for high-wear areas.
- Flexible: Remains pliable after application, preserving the flexibility of shoe soles.
- Waterproofing: Useful for waterproofing fabrics and shoes, increasing their lifespan.
Disadvantages Of Shoe Goo
Even though its strengths, Shoe Goo has some drawbacks:
- Strong Odor: Has a noticeable solvent smell that can be unpleasant during application.
- Cost: Generally more expensive compared to alternatives like rubber cement.
- Limited Availability: Less widely available than rubber cement, which may require some effort to find.
Advantages Of Rubber Cement
Rubber cement also has distinct benefits:
- Quick Fixes: Provides a fast and easy solution for minor repairs, especially on flexible materials.
- Easy To Remove: Designed for temporary bonds, allowing for easy removal without damaging the surfaces involved.
- Widely Available: Easy to find in most stores, making it a convenient choice for quick repairs.
Disadvantages Of Rubber Cement
But, rubber cement comes with its own set of limitations:
- Less Durable: Weaker bond strength compared to Shoe Goo, making it less suitable for long-term repairs.
- Limited Material Use: Best for bonding lightweight, flexible materials; not as effective on more rigid surfaces.
- Not Waterproof: Doesn’t offer waterproofing capabilities, reducing its effectiveness for outdoor or high-moisture applications.
| Feature | Shoe Goo | Rubber Cement |
|---|---|---|
| Use on Various Materials | Yes (rubber, wood, glass, etc.) | Limited to flexible materials |
| Bond Strength | High | Moderate |
| Abrasion Resistance | Yes (Styrene-butadiene) | No |
| Waterproof | Yes | No |
| Flexibility | High | Moderate |
| Odor | Strong (solvent smell) | Mild |
| Cost | Generally higher | Lower |
| Availability | Limited | Widely available |
| Removal | Permanent | Easy to remove (temporary) |
Understanding these pros and cons can help you choose the right adhesive for your specific shoe repair needs, ensuring the best results for your efforts.
Understanding the trade-offs between Shoe Goo and rubber cement can guide you to the right choice for your repair tasks. Choose based on the specific material, durability requirements, and application environment to ensure optimal results.
User Experiences
Customer Reviews And Feedback
Customer reviews reveal valuable insights into the performance of Shoe Goo and rubber cement for shoe repairs.
Shoe Goo:
- Versatility: Many users commend Shoe Goo for its adaptability in repairing various footwear components, such as reattaching soles and patching fabric.
- Durability: Reviews frequently highlight its long-lasting repairs, especially in high-wear conditions.
- Ease Of Use: Although effective, some users note the necessity for proper surface preparation to ensure successful repairs.
Rubber Cement:
- Quick Fixes: Users appreciate the convenience of rubber cement for temporary and fast repairs.
- Ease Of Application: Frequent positive mentions about its user-friendly application process.
- Durability Concerns: Several reviews point out its lack of long-term durability compared to Shoe Goo.
Common Issues Encountered
Understanding common issues can guide you in choosing between Shoe Goo and rubber cement.
Shoe Goo:
- Odor: Users often mention the strong smell during application.
- Application Complexity: Surface preparation is crucial, and improper techniques can lead to suboptimal results.
Rubber Cement:
- Bond Strength: Many users report that rubber cement’s bond is weaker and less durable.
- Material Compatibility: It works best on lightweight, flexible materials and may not be suitable for heavy-duty repairs.
By comparing user experiences and addressing common issues, you can make informed decisions for your specific repair needs.
Conclusion
Choosing between Shoe Goo and rubber cement depends on your specific needs and the type of repair you’re looking to accomplish. If you need a durable, flexible, and long-lasting solution, Shoe Goo is your go-to adhesive. It’s perfect for high-wear areas and provides excellent bonding and sealing capabilities.
On the other hand, if you’re after a quick, temporary fix, rubber cement offers ease of use and convenience. It’s ideal for lightweight materials and non-damaging applications but may not hold up well over time.
Understanding the strengths and limitations of each adhesive will help you make an well-informed choice for your shoe repair projects. Whether you prioritize durability or convenience, both Shoe Goo and rubber cement have their unique advantages to offer.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which adhesive is more durable, Shoe Goo or rubber cement?
Shoe Goo is more durable compared to rubber cement. It offers strong bonding properties, flexibility, and abrasion resistance, making it suitable for long-term shoe repairs, especially in high-wear areas.
How long does it take for Shoe Goo to cure fully?
Shoe Goo typically cures in about 24 hours and reaches maximum strength within 48 to 72 hours. For best results, make sure the surface is clean and dry before application.
Is rubber cement good for long-term shoe repairs?
No, rubber cement is generally not suitable for long-term shoe repairs. It provides a weaker bond designed for easy removal and works best for temporary fixes and lightweight materials.
Can Shoe Goo be used on materials other than shoes?
Yes, Shoe Goo is versatile and can be used on various materials beyond shoes, including leather, rubber, and even fabrics. It is also effective for waterproofing and sealing.
Does rubber cement waterproof materials?
No, rubber cement does not offer waterproofing capabilities. It is best for quick, temporary fixes and crafting applications where a permanent, waterproof bond is not required.
What are the common issues with using Shoe Goo?
The common issues with using Shoe Goo include its strong odor and the need for precise application. It may also be more expensive and harder to find compared to rubber cement.
How do you apply rubber cement for the best results?
For best results, apply rubber cement to both surfaces you wish to bond. Allow the adhesive to dry to a tacky state before pressing the surfaces together. This method provides a stronger bond.
Are there any user reviews comparing Shoe Goo and rubber cement?
Yes, users commend Shoe Goo for its durability and versatility, though proper surface preparation is necessary. Rubber cement is appreciated for its quick application and easy removal but is criticized for its lack of long-term durability.