Best Adhesive for Floor Tiles: Find the Perfect Match for Your Project
Choosing the right adhesive for floor tiles can make or break your tiling project. Whether you’re renovating your kitchen or laying tiles in your bathroom, the adhesive you select ensures your tiles stay in place and withstand daily wear and tear. With so many options out there, it’s crucial to know which adhesive works best for your specific needs.
Key Takeaways
- Understand Tile Adhesives: Different types of tile adhesives, including thin-set mortar, epoxy, and mastic, serve various purposes and conditions. Thin-set is versatile, epoxy is highly durable, and mastic is easy to apply but not suitable for wet areas.
- Importance of Substrate and Tile Type: The choice of adhesive should match the substrate (concrete, plywood, etc.) and the tile material (ceramic, porcelain, natural stone) to ensure proper bonding and durability.
- Application Techniques Matter: Proper surface preparation, mixing, and application techniques are crucial for a successful tiling project. Clean the surface thoroughly, mix the adhesive correctly, and apply evenly using a notched trowel.
- Consider Environmental Factors: For areas with high moisture or temperature variations, such as bathrooms or outdoor spaces, use moisture-resistant or heat-resistant adhesives to ensure the tiles stay intact.
- Adhesive Types for Specific Scenarios: Choose the appropriate adhesive based on the project’s requirements. For example, use thin-set mortar in moist areas, epoxy for high-stress environments, and flexible adhesives for high-traffic areas.
- Avoid Common Mistakes: Ensure proper surface cleaning and leveling, use the correct adhesive for the specific tile and environment, and follow precise mixing and application techniques to prevent issues like tile lifting or poor adhesion.
What Is Tile Adhesive?
Tile adhesive, also known as tile glue or tile mortar, is a crucial material that bonds tiles to surfaces, ensuring they remain securely in place on floors or walls. Its versatility and strength depend on the type and application.

Types of Tile Adhesives:
-
Thin-Set Mortar:
- Composition: Made from cement, fine sand, and water-retaining agents.
- Forms: Available in unmodified and modified forms. Modified thin-set includes liquid latex polymers for enhanced bonding strength and flexibility.
- Usage: Ideal for most tile installations, providing a strong bond and durability on various surfaces.
-
Mastic:
- Composition: Premixed adhesive typically made from acrylic.
- Advantages: Easy to use, ready-to-apply directly from the container.
- Limitations: Not suitable for flooring or wet areas due to its lack of durability and moisture resistance. Best used for smaller wall tile installations.
-
Epoxy:
- Composition: A durable, two-part adhesive known for its excellent bonding strength and chemical resistance.
- Advantages: Highly durable and stain-resistant, making it suitable for heavy or large-format tiles and areas prone to staining or chemicals.
- Challenges: More complex to apply and generally more expensive compared to other options. Requires precise mixing and application.
Key Factors for Choosing Tile Adhesive
Substrate Type: The surface receiving the tile plays a significant role in adhesive selection. Concrete, drywall, plywood, or cement board substrates each have specific adhesive requirements.
Tile Material: Different materials like ceramic, porcelain, glass, or natural stone may need specific adhesives to ensure proper bonding and longevity.
Tile Size: Larger tiles often require stronger adhesives such as modified thin-set or epoxy to support their weight and prevent them from slipping.
Detailed Comparison of Tile Adhesives
| Type | Strength | Water Resistance | Ease of Use | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thin-Set Mortar | High | Moderate to High | Requires Mixing | Floors, Walls, Indoor, Outdoor |
| Mastic | Moderate | Low | Premixed (Easy) | Small Wall Tiles, Dry Areas |
| Epoxy | Very High | Very High | Requires Precision | Heavy/ Large Tiles, High-Stress Areas |
- Preparation: Clean the surface thoroughly, ensuring it’s free from dust, grease, and debris.
- Mixing: For thin-set and epoxy, follow manufacturer instructions for mixing ratios and techniques.
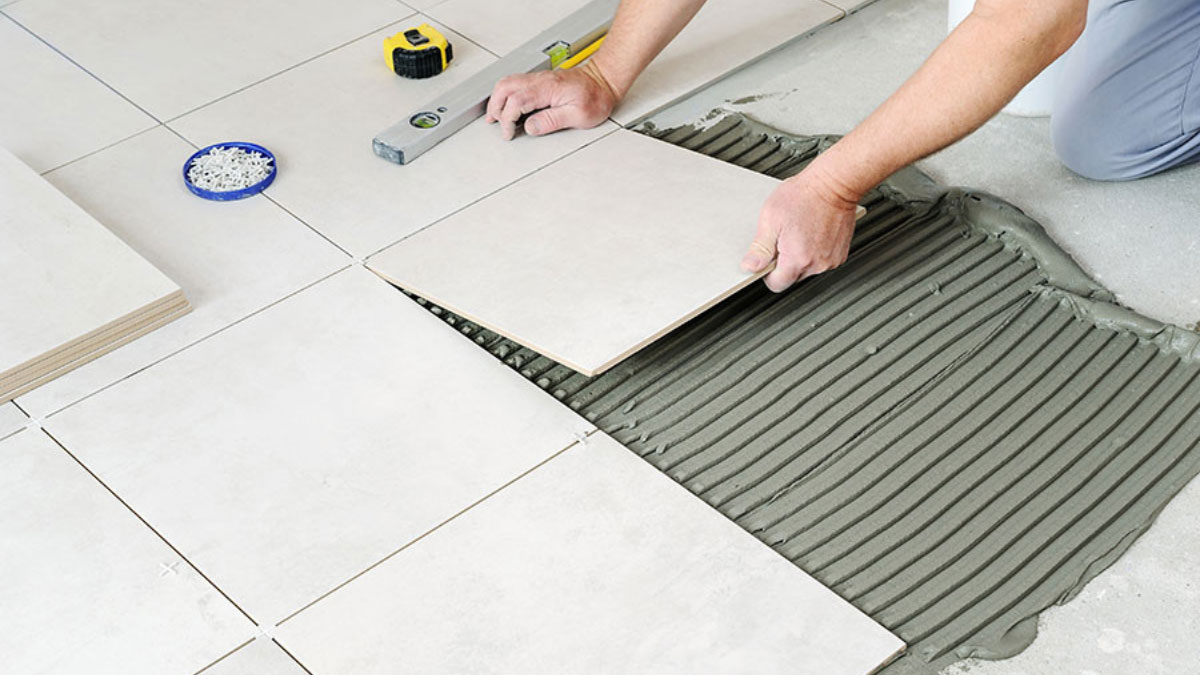
- Application: Use a notched trowel to spread the adhesive evenly, creating ridges to ensure good contact with the tile.
- Setting: Allow adequate time for the adhesive to set and cure before grouting or walking on the tiles.
Choosing the right tile adhesive is essential for a successful tiling project. Ensuring you match the adhesive type to your specific needs will help achieve a durable, long-lasting finish.
Types of Floor Tile Adhesives
When selecting floor tile adhesives, understanding the different types and their applications ensures a strong, durable bond. Here are the primary types to consider:
Thinset Mortar
Composition:
Thinset mortar consists of cement, fine sand, and water-retaining agents. It comes in two types:
- Unmodified Thinset: Lacks polymers.
- Modified Thinset: Contains added polymers (latex) for improved bonding.
Usage:
Thinset is popular for floors and areas with high moisture like bathrooms and kitchens. It’s suitable for both walls and floors, especially in wet or damp areas.
Advantages:
- Cost-effective
- Readily available
- Moisture-resistant
- Available in gray and white
Drawbacks:
- Unmodified thinset can be challenging to work with.
- Requires more material for a firm hold.
Epoxy Tile Adhesives
Composition:
Epoxy adhesives contain resin and hardener, forming a strong, chemical-resistant bond once mixed.
Usage:
Ideal for areas exposed to chemicals, heavy loads, and high moisture. Common in industrial and commercial settings, kitchens, and bathrooms.
Advantages:
- Exceptional bonding strength
- Chemical-resistant
- Water-resistant
- Suitable for challenging environments
Drawbacks:
- More expensive than other types
- Requires precise mixing and application
Polymer-Modified Cementitious Tile Adhesives
Composition:
These adhesives combine cement, fine sand, and polymer additives (latex), enhancing flexibility and adhesion.
Usage:
Suitable for various substrates, including concrete, plywood, and existing tiles. Great for indoor and outdoor applications.
Advantages:
- Enhanced adhesion
- Flexible and durable
- Suitable for numerous substrates
- Good for interior and exterior use
Drawbacks:
- More costly than traditional cementitious adhesives
- Requires careful preparation and handling
Mastic Tile Adhesive
Composition:
Mastic adhesive is an organic adhesive, usually premixed, with a paste-like consistency.
Usage:
Best for dry, interior settings like backsplashes and accent walls. Not recommended for floors or wet areas.
Advantages:
- Easy to apply
- Ready-to-use
- Strong initial bond
Drawbacks:
- Not suitable for wet areas or floors
- Limited temperature resistance
| Adhesive Type | Composition | Ideal For | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thinset Mortar | Cement, fine sand, water-retaining agents | Wet and damp areas (bathrooms, kitchens) | Inexpensive, moisture-resistant, versatile | Unmodified can be tricky, needs more material |
| Epoxy Tile Adhesives | Resin and hardener | Industrial, commercial, and high-moisture areas | High strength, chemical and water-resistant | Expensive, requires precision |
| Polymer-Modified Cementitious Tile Adhesives | Cement, fine sand, polymer additives | Various substrates, indoor and outdoor | Enhanced adhesion, flexible, durable | Costlier, careful handling needed |
| Mastic Tile Adhesive | Organic premixed compound | Dry, interior settings (backsplashes) | Easy to apply, strong initial bond | Not for wet areas or floors, temperature limits |
Understanding these adhesive types helps ensure a successful tiling project. Consider the specific requirements of the area and the properties of each adhesive to make the best choice.
Choosing the Right Adhesive
Selecting the correct adhesive is pivotal for floor tile installation. It ensures durability and maintains the integrity of the design. Here, we investigate into adhesive recommendations based on tile types, substrates, and environmental conditions.
Tile Type
- Porcelain and Ceramic Tiles:
- Recommended Adhesive: A flexible and durable adhesive. Look for products labeled “porcel bond” or those from reputable brands like Mapei.
- Advantages: These adhesives provide necessary strength and flexibility required for porcelain and ceramic tiles.
- Examples: Mapei flexible adhesive.
Substrate and Surface Conditions
- Wood Substrate:
- Preparation: Use a tile backing board to ensure an even surface.
- Recommended Adhesive: Thinset mortar.
- Details: Secure the wood substrate with plywood, screwed down at 150mm centers.
- Plywood Substrate:
- Specifications: Ensure the plywood is at least 9mm thick.
- Recommended Adhesive: A flexible adhesive to accommodate movement in the plywood.
- Details: Securely screw down the plywood to avoid any shifts.
Environmental Factors
Consider the room’s moisture level and temperature fluctuations:
- High Moisture Areas: Use water-resistant adhesives, such as epoxy, in bathrooms and kitchens.
- Temperature Variations: Flexible adhesives are essential in areas with significant temperature changes to account for expansion and contraction.
Adhesive Comparison Table
| Adhesive Type | Best For | Key Properties | Example Brands |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thin-set Mortar | General Use | Cost-effective, Moisture Resistant | Custom Building Products, Schluter, Mapei |
| Epoxy Adhesive | High-traffic, Moisture-prone areas | Exceptional Bond Strength, Chemical Resistance | Latapoxy, Laticrete |
| Polymer-modified Cementitious Adhesive | Porcelain, Ceramic | Enhanced Flexibility, Strength | Mapei, Bostik |
| Mastic Adhesive | Dry Areas | User-friendly, Quick Application | Roberts, TEC |
Action Point
Choose adhesives based on the specific requirements of your tile type and installation conditions. This ensures a successful, durable tiling project.
Preparation and Application Tips
Proper preparation and precise application are crucial for achieving a durable, professional tile installation. Following these tips can help ensure your project succeeds.
Surface Preparation
To ensure optimal adhesion, the surface must be clean, dry, and level.
- Clean the Surface: Remove dirt, dust, grease, and old adhesive residues.
- Check for Levelness: Use a leveling compound to correct uneven areas.
- Prime the Surface: Apply a primer to porous surfaces to seal them.
Mixing and Application Techniques
Following the correct mixing and application techniques can significantly affect adhesive performance.
- Read Manufacturer Instructions: Always follow the specific mixing ratio provided by the manufacturer.
- Use a Mechanical Mixer: For a consistent mix, use a mechanical mixer rather than mixing by hand.
- Application Tools: Use a notched trowel for even adhesive spread.
- Apply the Adhesive: Spread adhesive on the surface, press tiles firmly in place, and adjust as needed.
- Set Time: Allow the adhesive to set as advised, usually 24-48 hours, before grouting.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Avoid these common pitfalls to ensure your tile installation lasts:
- Using Incorrect Adhesive: Choose the adhesive suitable for your tile type and installation environment.
- Insufficient Surface Preparation: Neglecting surface cleaning or leveling can lead to poor adhesion and uneven tiles.
- Improper Mixing: Incorrect mixing ratios can compromise adhesive strength.
- Application Errors: Inconsistent adhesive spreading can cause tiles to lift or shift.
By adhering to these guidelines, you can achieve a professional, long-lasting tile floor installation.
Best Adhesives for Different Scenarios
Selecting the right adhesive for floor tiles ensures durability and strength. Different scenarios call for specific adhesives to achieve optimal results.
Indoor Projects
For indoor tile installations, adhesives must provide strong bonding and accommodate minor substrate movements.
- Thin-Set Mortar
- Description: Thin-set mortar, a mix of cement, fine sand, and water-retaining agents, is common. Modified versions include polymers for better bonding and flexibility.
- Advantages: Works well in moisture-prone areas like bathrooms and kitchens. Suitable for various substrates such as plywood and cement.
- Application: Ensure the substrate is level and clean. Apply with a notched trowel per manufacturer instructions.
- Flexible Adhesives
- Description: Ideal for porcelain and large-format tiles. These adhesives contain polymers to provide elasticity.
- Advantages: Prevents cracking in the tiles due to substrate movement. Best for high-traffic areas.
- Application: Follow guidelines for substrate preparation and adhesive mixing to ensure strong bonding.
Outdoor Projects
Outdoor tile projects need adhesives that can withstand environmental factors such as temperature changes and moisture.
- Epoxy Adhesives
- Description: Composed of resin and hardener, epoxy adhesives offer robust bonding and chemical resistance.
- Advantages: Highly durable and resistant to moisture and temperature variations. Suitable for patios and outdoor decks.
- Application: Mix resin and hardener accurately. Apply evenly to ensure complete coverage.
- Polymer-Modified Cementitious Adhesives
- Description: These adhesives are enhanced with polymers to improve flexibility and adhesion.
- Advantages: Excellent for areas exposed to weather changes. Provides strong adhesion on concrete and wooden substrates.
- Application: Prepare the surface by cleaning and ensuring it’s level. Mix the adhesive per manufacturer instructions and apply with a notched trowel.
Specialized Applications
Certain installations require specialized adhesives to address unique challenges.
- Mastic Adhesive
- Description: A ready-to-use adhesive ideal for dry areas.
- Advantages: Easy to apply without mixing. Suitable for wall tiles and light-use indoor floors.
- Application: Ensure the surface is dry and clean. Apply directly from the container.
- Heat-Resistant Adhesives
- Description: Formulated to withstand high temperatures.
- Advantages: Perfect for areas near fireplaces or heated floors. Prevents degradation due to heat.
- Application: Follow specific guidelines for heat-resistant applications. Ensure even distribution for best results.
Adhesive Comparison Table
| Adhesive Type | Indoor Use | Outdoor Use | Specialized Application | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thin-Set Mortar | Yes | No | No | Strong bonding, flexible, moisture-resistant |
| Flexible Adhesives | Yes | No | No | Prevents cracking, ideal for high-traffic areas |
| Epoxy Adhesives | No | Yes | Yes | Robust bonding, chemical-resistant, moisture and temperature-resistant |
| Polymer-Modified Cementitious Adhesives | Yes | Yes | No | Flexible, strong adhesion for outdoor use |
| Mastic Adhesive | Yes | No | No | Ready-to-use, ideal for dry areas |
| Heat-Resistant Adhesives | Yes | No | Yes | High-temperature resilience, prevents heat-induced damage |
Choosing the correct adhesive ensures a durable and lasting tile installation. Match the adhesive type to your project to achieve the best results.
Conclusion
Choosing the right adhesive for your floor tiles is crucial for ensuring a durable and successful installation. By understanding the various adhesive options and their specific applications, you can make an well-informed choice that suits your project’s needs. Whether you’re working on a kitchen, bathroom, or outdoor area, selecting the appropriate adhesive will help your tiles withstand everyday use and environmental factors.
Always prioritize proper surface preparation and follow manufacturer instructions for mixing and application. Avoid common mistakes to achieve a professional finish that lasts. With the right adhesive and careful execution, your tiling project will stand the test of time.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is tile adhesive?
Tile adhesive, also known as tile glue or tile mortar, is a material used to bond tiles to surfaces. It ensures tiles remain secure and durable against everyday use.
What are the different types of tile adhesives?
Common types of tile adhesives include thin-set mortar, mastic, epoxy, and polymer-modified cementitious adhesives. Each type has unique compositions, advantages, and ideal applications.
How do I choose the right tile adhesive?
Choose the adhesive based on substrate type, tile material, and environmental conditions. For example, thin-set mortar is suitable for most indoor applications, while epoxy is ideal for outdoor and high-moisture areas.
Can I use mastic adhesive in wet areas?
No, mastic adhesive is not suitable for wet areas. It’s best used in dry areas because it lacks moisture resistance compared to other adhesives like thin-set mortar or epoxy.
What is the best adhesive for outdoor tile projects?
Epoxy adhesives and polymer-modified cementitious adhesives are ideal for outdoor projects due to their durability and resistance to environmental factors.
How thick should tile adhesive be for floor tiles?
For floor tiles, aim for a minimum adhesive thickness of 3-5mm. Thicker layers may be needed for larger tiles to ensure a strong bond.
Why won’t my self-adhesive floor tiles stick?
Self-adhesive tiles may not stick if the surface is wet, dusty, or uneven. Proper surface preparation, including cleaning and leveling, is essential for adhesive tiles to bond properly.
What should be done before applying tile adhesive?
Before applying tile adhesive, clean and prime the surface, ensure it is level, and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for mixing and application. This preparation is crucial for a durable installation.
Are there specific adhesives for high-temperature environments?
Yes, heat-resistant adhesives are recommended for high-temperature environments. These adhesives can withstand extreme temperatures without losing their bonding strength.